The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is here, but with new technology comes new challenges. Are electric vehicles truly the future, or do they come with hidden headaches?
1. Battery Life and Degradation
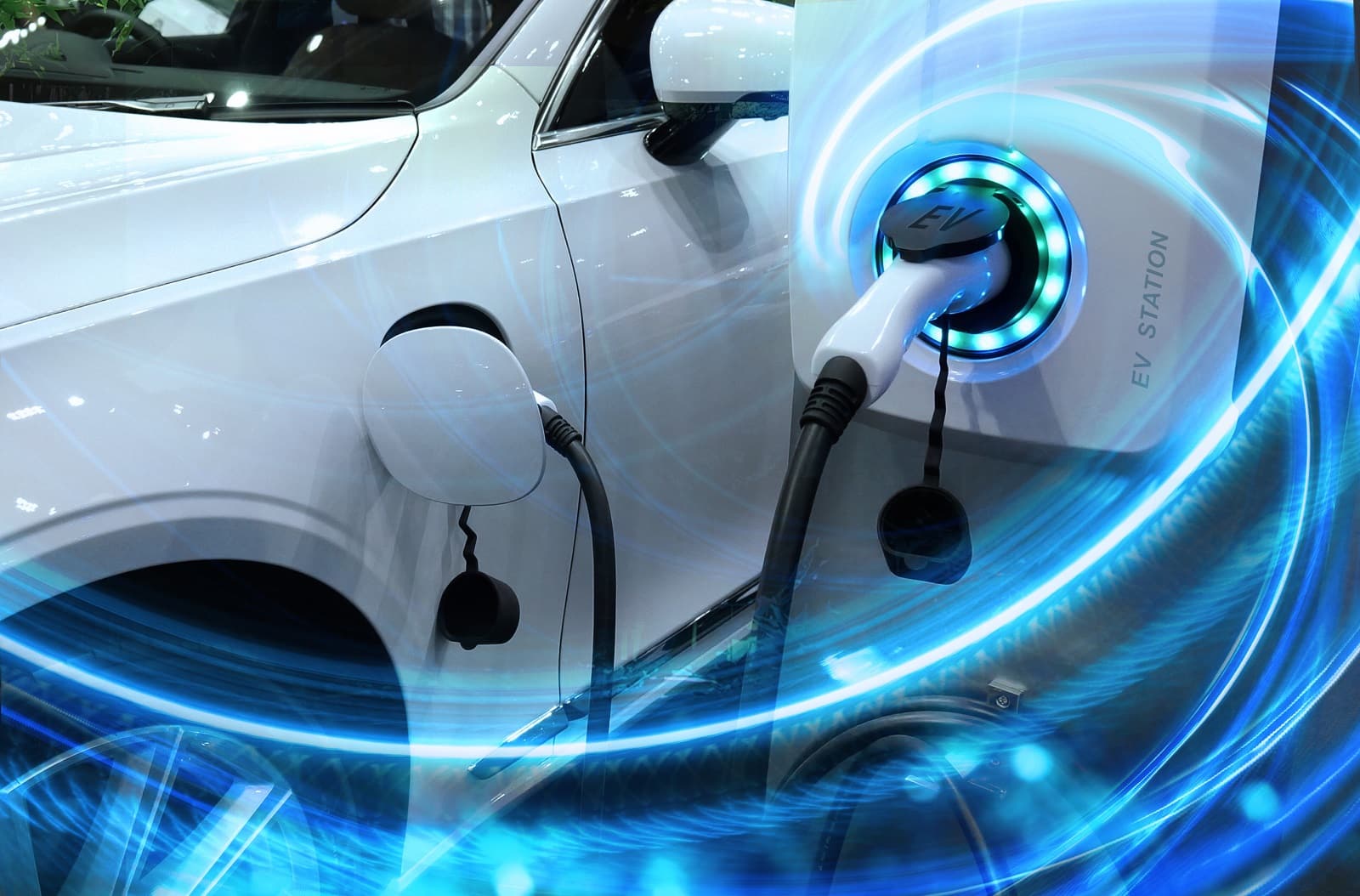

Image Credit: Shutterstock / buffaloboy
The heart of an EV is its battery, and battery degradation over time is a significant concern. According to a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, most EV batteries lose about 2.3% of their capacity annually, meaning reduced range over time. This degradation is affected by climate, charging habits, and usage.
2. Charging Infrastructure

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Darunrat Wongsuvan
While charging at home is convenient, the lack of widespread, reliable public charging infrastructure can make long trips challenging. As of 2023, the U.S. had over 50,000 charging stations, but many are slow chargers or are located in inconvenient places, causing range anxiety for drivers, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
3. Limited Range

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Tada Images
Although EV ranges are improving, they still fall short of most gasoline-powered vehicles. The average range for new EVs is around 250 miles per charge, according to the EPA. This is fine for daily commutes, but longer road trips require careful planning and frequent stops.
4. Winter Performance
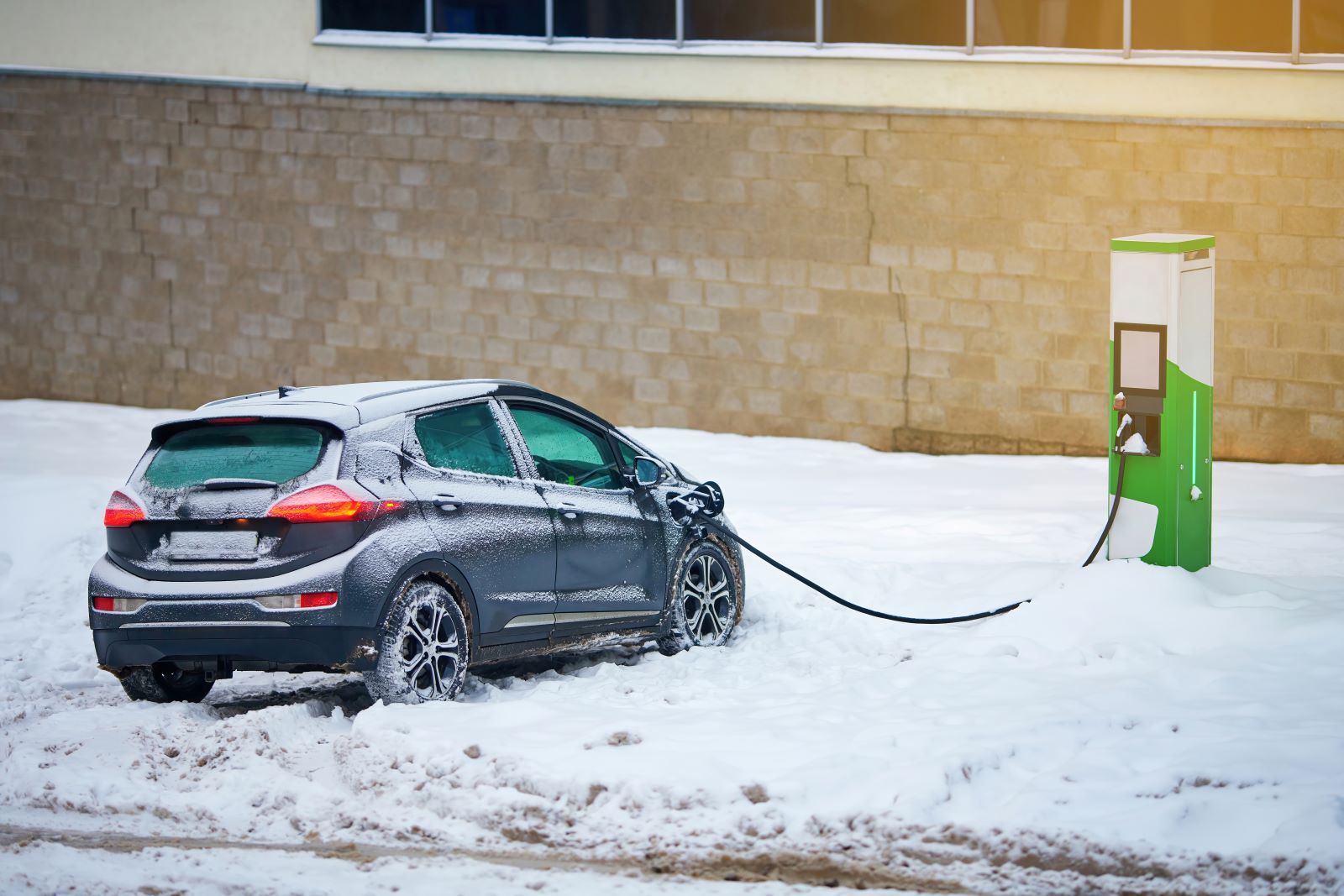

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Tricky_Shark
Cold weather negatively impacts EV performance. According to AAA, cold temperatures can reduce an EV’s range by up to 41% due to increased battery drain from heating systems and the reduced efficiency of lithium-ion batteries in cold weather.
5. High Initial Costs

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Roschetzky Photography
Although EVs have lower operating costs, their upfront prices are still high compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Kelley Blue Book reports that as of 2023, the average price of an EV was over $58,000, making them less accessible to the average buyer.
6. Repair and Maintenance Complexity
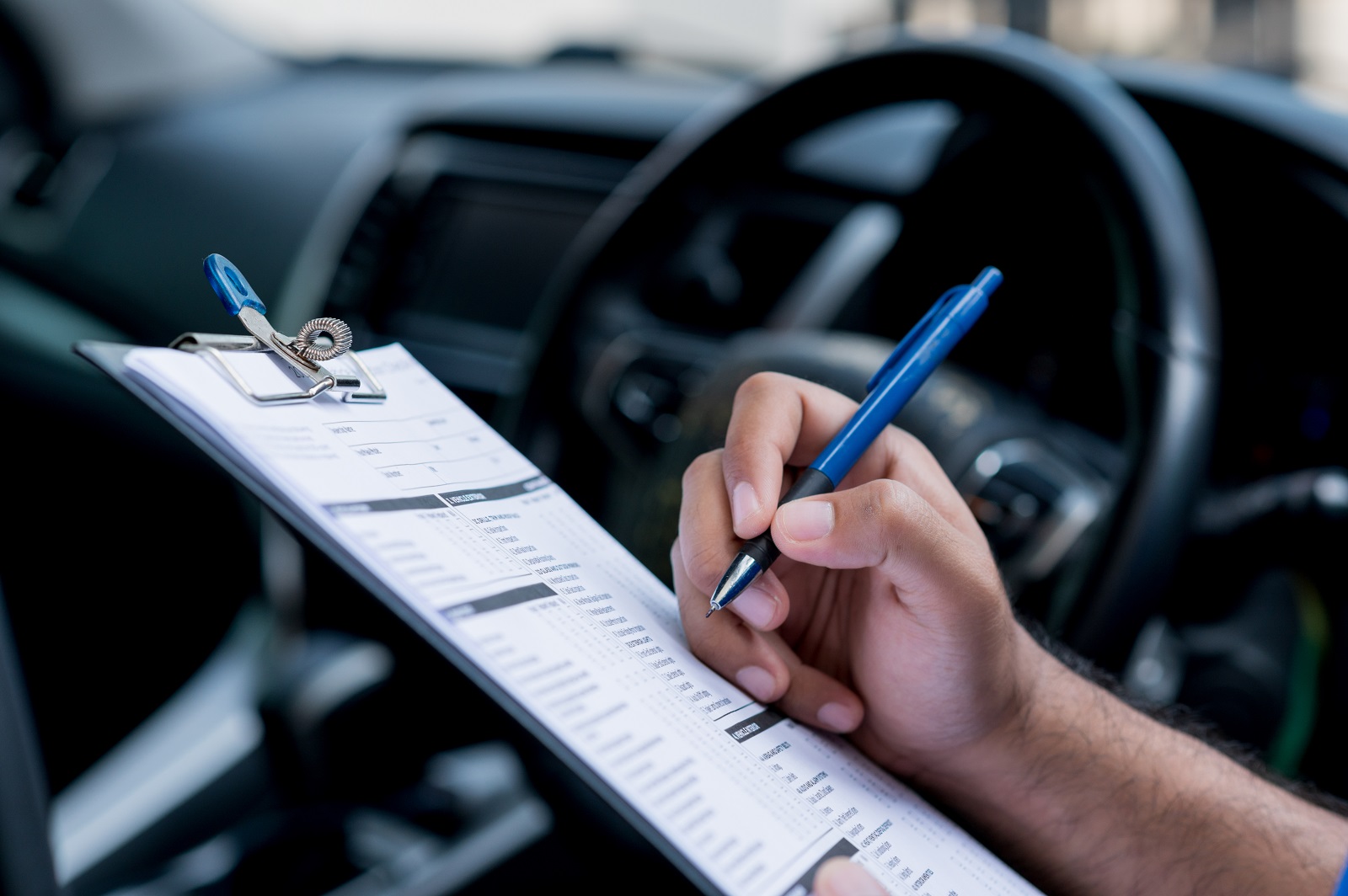

Image Credit: Shutterstock / GBJSTOCK
While EVs have fewer moving parts than traditional cars, repairs can be more complex and expensive. According to Consumer Reports, specialized parts and trained technicians are not as widely available, leading to longer repair times and higher costs for specific issues like battery replacements or electric motor repairs.
7. Battery Replacement Costs
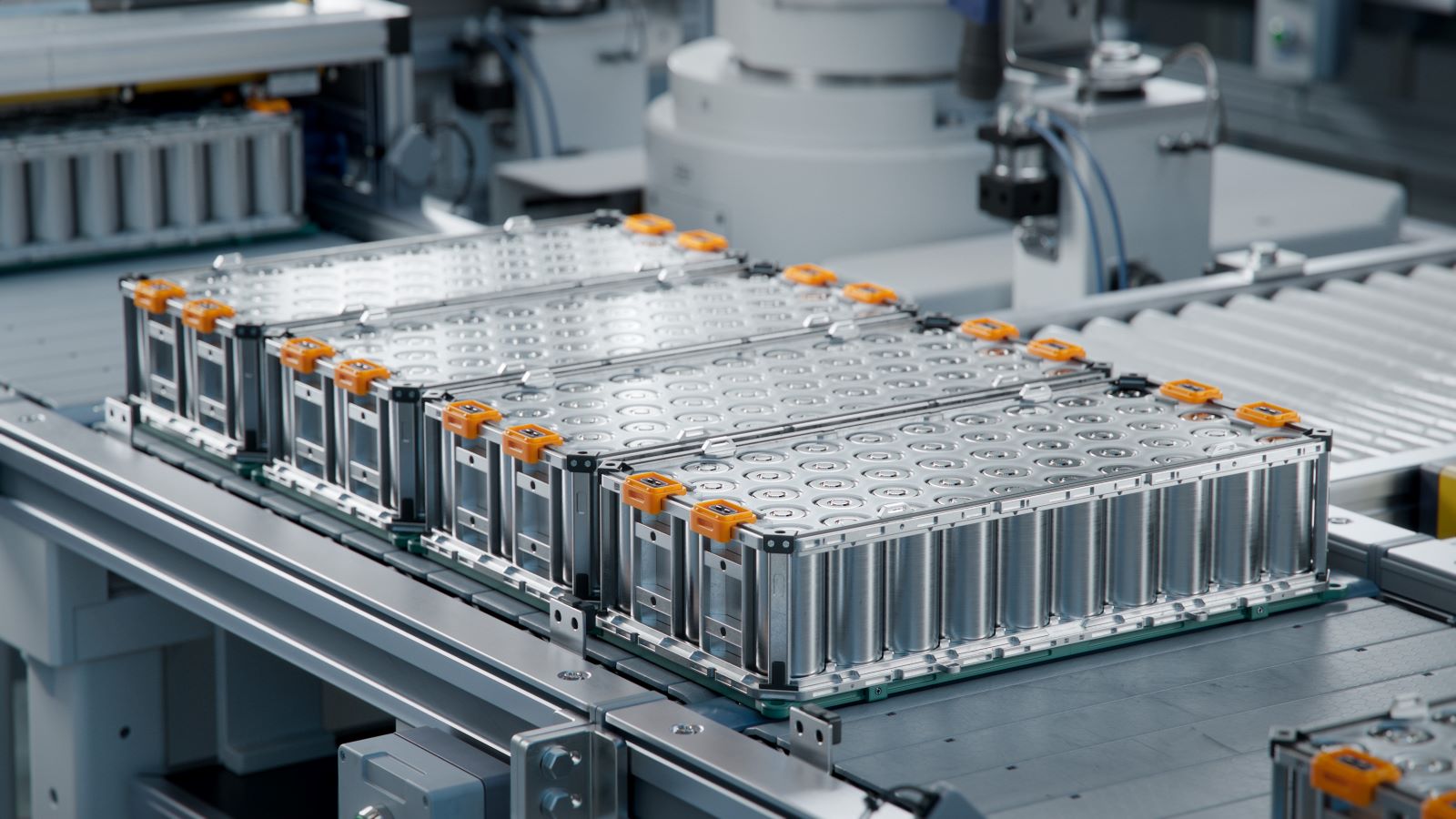
Image Credit: Shutterstock / IM Imagery
Battery replacement is one of the most expensive repairs an EV owner can face. On average, replacing an EV battery costs between $5,000 and $15,000, depending on the model, according to Recurrent Auto, a company that tracks EV battery performance. This can be a major expense, especially as vehicles age.
8. Software and Tech Issues

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Gorodenkoff
Many EVs rely heavily on software for everything from performance management to infotainment. While this can make the driving experience smoother, it also opens the door to glitches and bugs. Tesla owners, for example, have reported software issues that range from screen freezes to autopilot malfunctions, as noted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
9. Charging Time
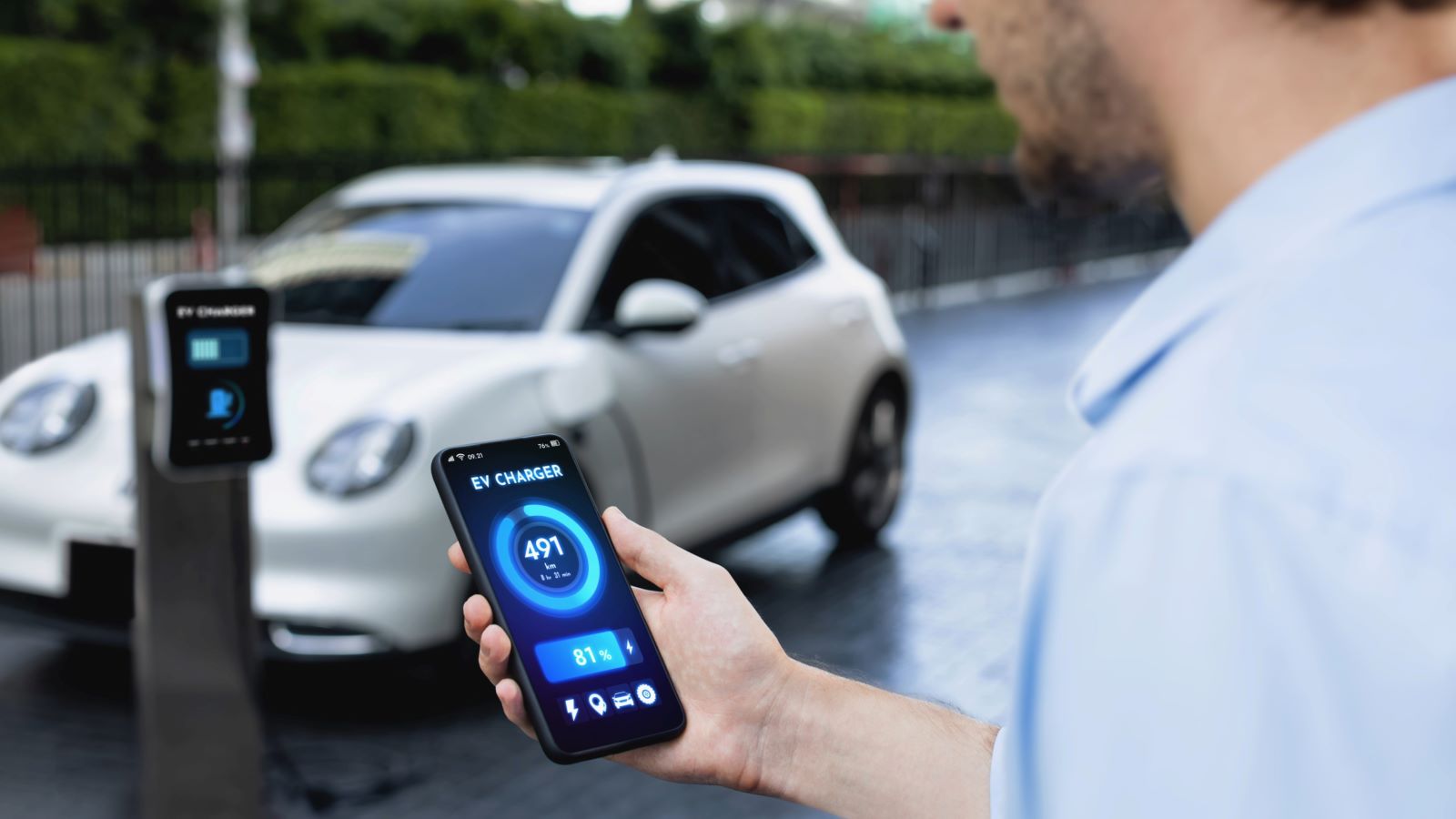

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Owlie Productions
Charging an EV takes significantly longer than filling up a gas tank. Even with fast chargers, it can take 30 minutes to an hour to reach 80% charge, and home charging on a standard outlet can take up to 24 hours for a full charge. This can be inconvenient for those who are used to the quick refuel times of ICE vehicles.
10. Dependence on Specific Charging Networks
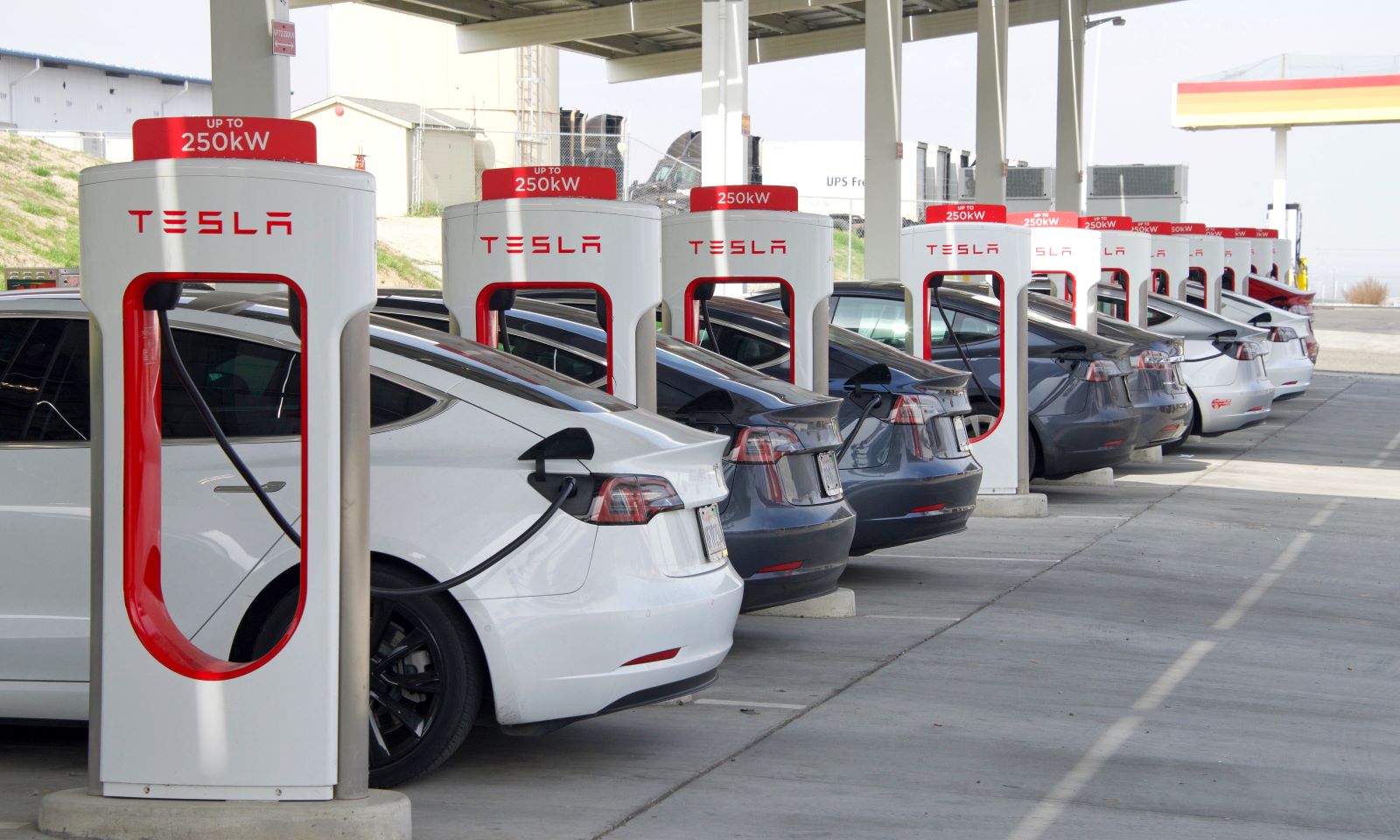

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Sheila Fitzgerald
Some EV manufacturers, like Tesla, have their own proprietary charging networks, which limits where you can charge your vehicle. While Tesla’s Supercharger network is extensive, it isn’t compatible with non-Tesla EVs without an adapter, creating potential barriers for non-Tesla drivers.
11. Battery Fires and Safety Concerns

Image Credit: Shutterstock / T. Schneider
Battery fires, though rare, are a serious concern with EVs. Lithium-ion batteries, when damaged or overheated, can catch fire, and these fires are notoriously difficult to extinguish. The NHTSA has investigated several high-profile EV battery fires, raising concerns about safety standards.
12. Limited Availability of Repair Shops
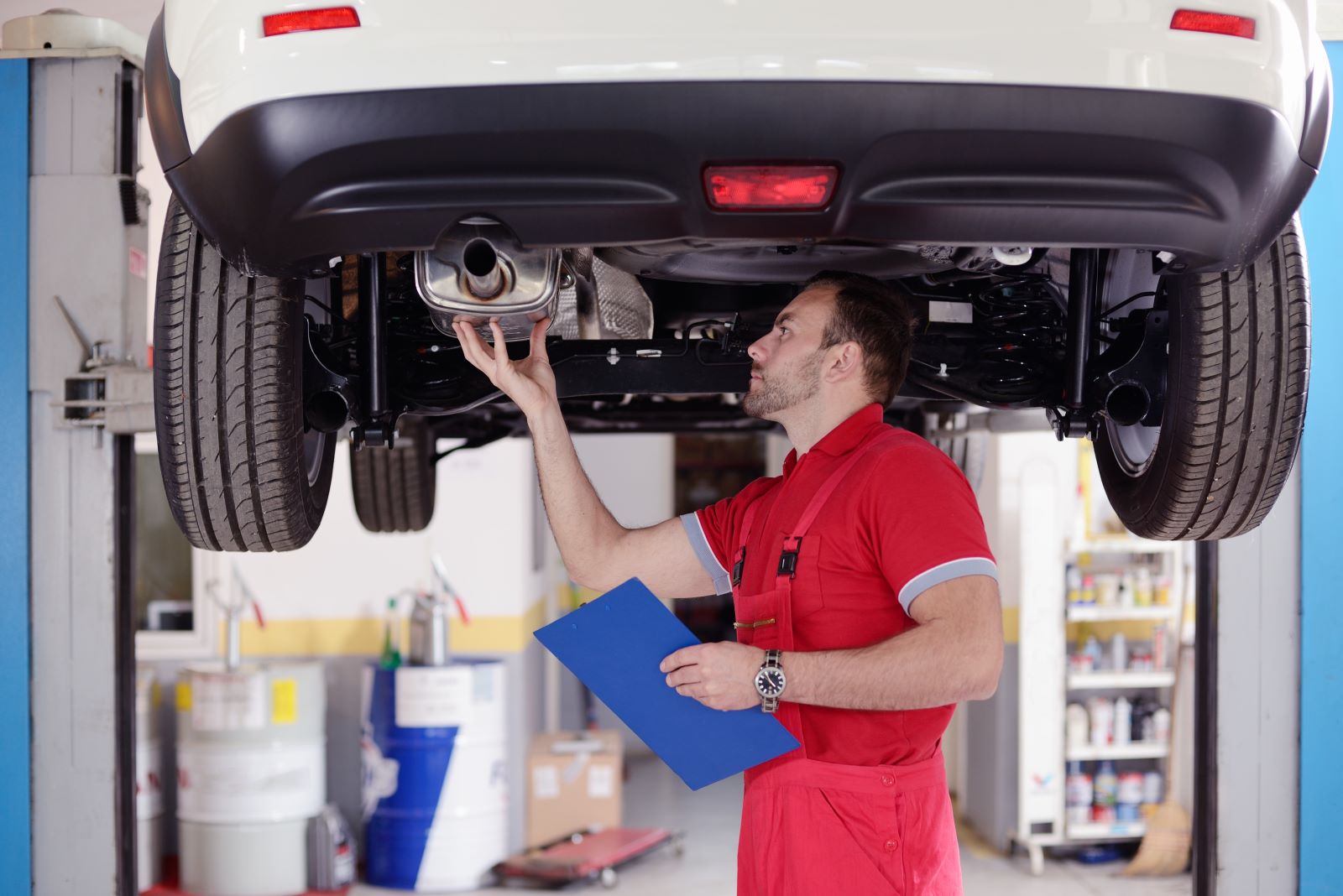

Image Credit: Shutterstock / BhFoton
EV-specific repair shops are still relatively scarce. According to the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), fewer mechanics are trained to service electric vehicles, which means owners may need to travel farther for repairs or deal with longer wait times.
13. Software Updates and Over-the-Air Fixes
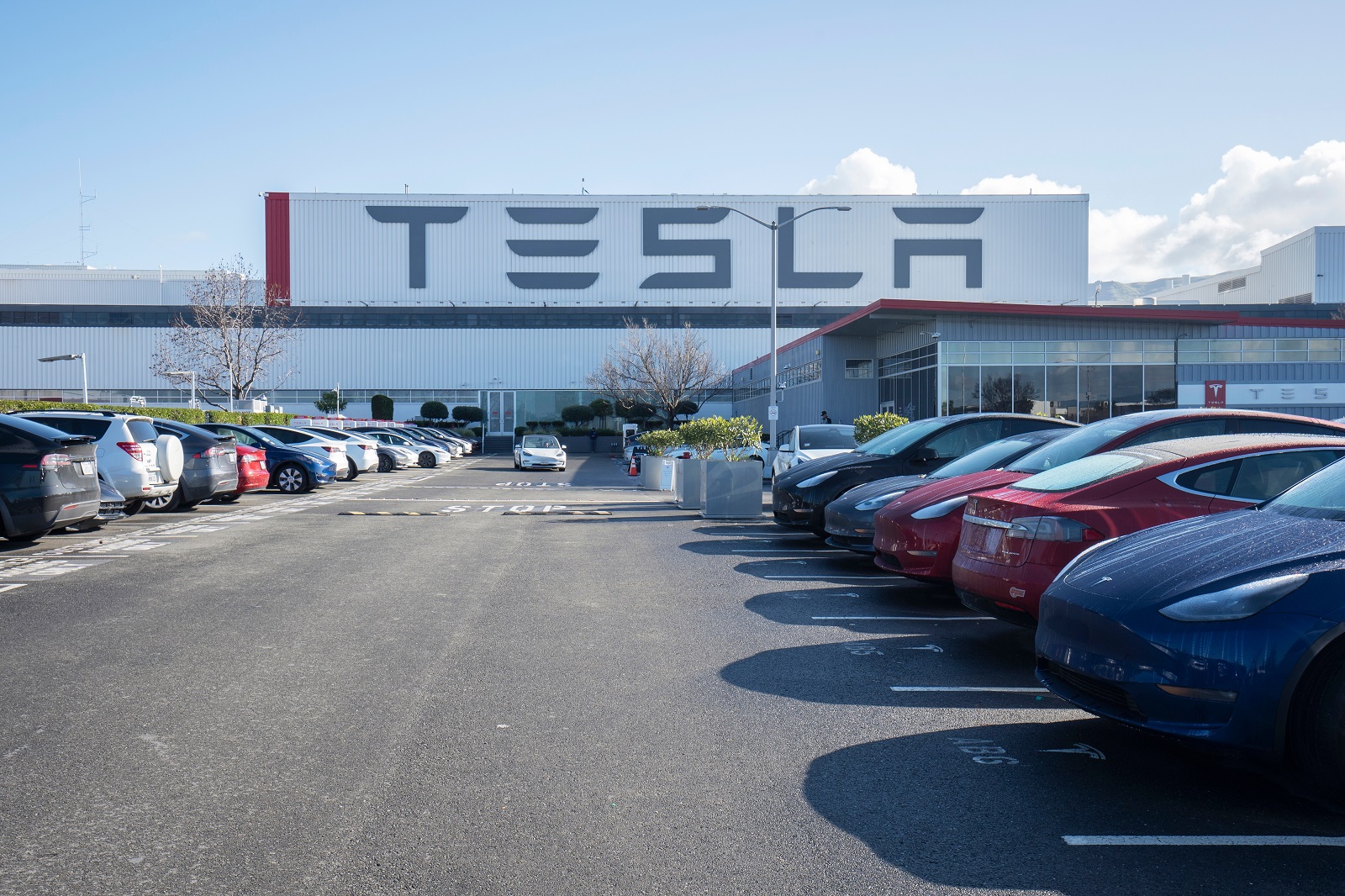

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Tada Images
One of the advantages of EVs is their ability to receive over-the-air software updates. Tesla leads the way in this area, often fixing issues remotely without requiring a trip to the dealership. However, these updates can also cause new problems, and some owners have reported that updates can even temporarily disable certain vehicle functions.
14. Environmental Concerns Over Battery Production

Image Credit: Shutterstock / noriox
While EVs are touted as environmentally friendly, the production of lithium-ion batteries has its own environmental impact. Mining for materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be harmful to ecosystems and often takes place in countries with lax environmental regulations, raising ethical concerns, according to a report by Amnesty International.
15. Resale Value

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Tada Images
EVs tend to depreciate faster than ICE vehicles, partly due to concerns about battery life and the rapid pace of technological advancement. According to Kelley Blue Book, the average EV loses about 60% of its value after five years, compared to 40% for a typical ICE vehicle.
16. Charging Costs and Utility Bills
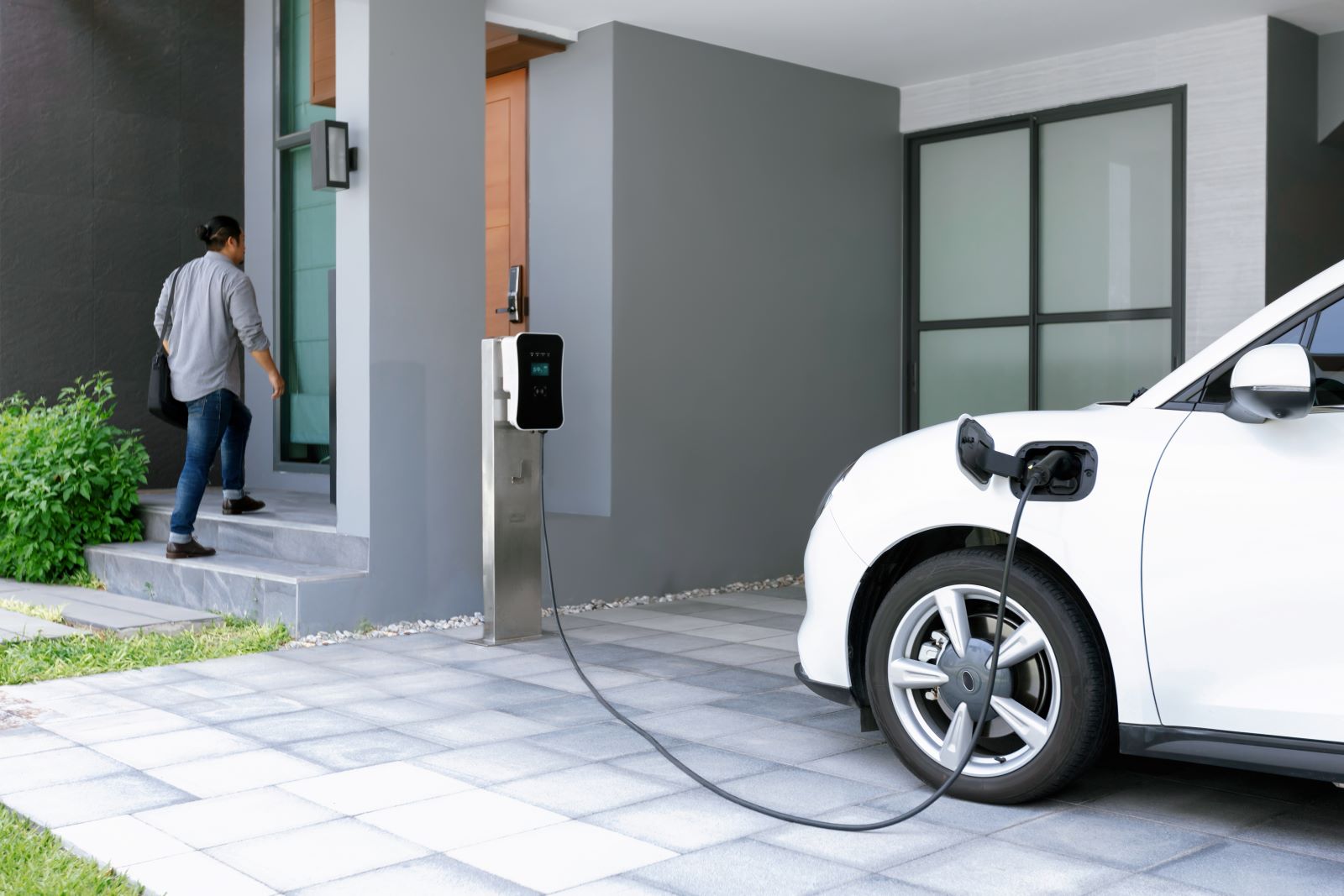

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Owlie Productions
While charging at home is cheaper than filling up at the pump, it can still lead to higher electricity bills. In states with higher electricity rates, the cost savings of driving an EV can diminish, especially if you frequently use public fast chargers, which often charge premium rates.
17. Towing and Hauling Limitations

Image Credit: Shutterstock / antoniodiaz
For those who need a vehicle for towing or heavy hauling, many EVs fall short. The extra strain of towing can significantly reduce an EV’s range, making it less practical for long-distance hauling. Tesla’s Cybertruck and Rivian’s R1T are attempting to address this issue, but range limitations persist.
18. Limited Model Availability

Image Credit: Shutterstock / totojang1977
While the EV market is expanding, the variety of models available is still limited compared to the vast array of gasoline and diesel options. This can make it difficult for consumers to find an EV that meets all their needs, whether it’s for performance, size, or budget.
19. Cold Battery Charging Issues
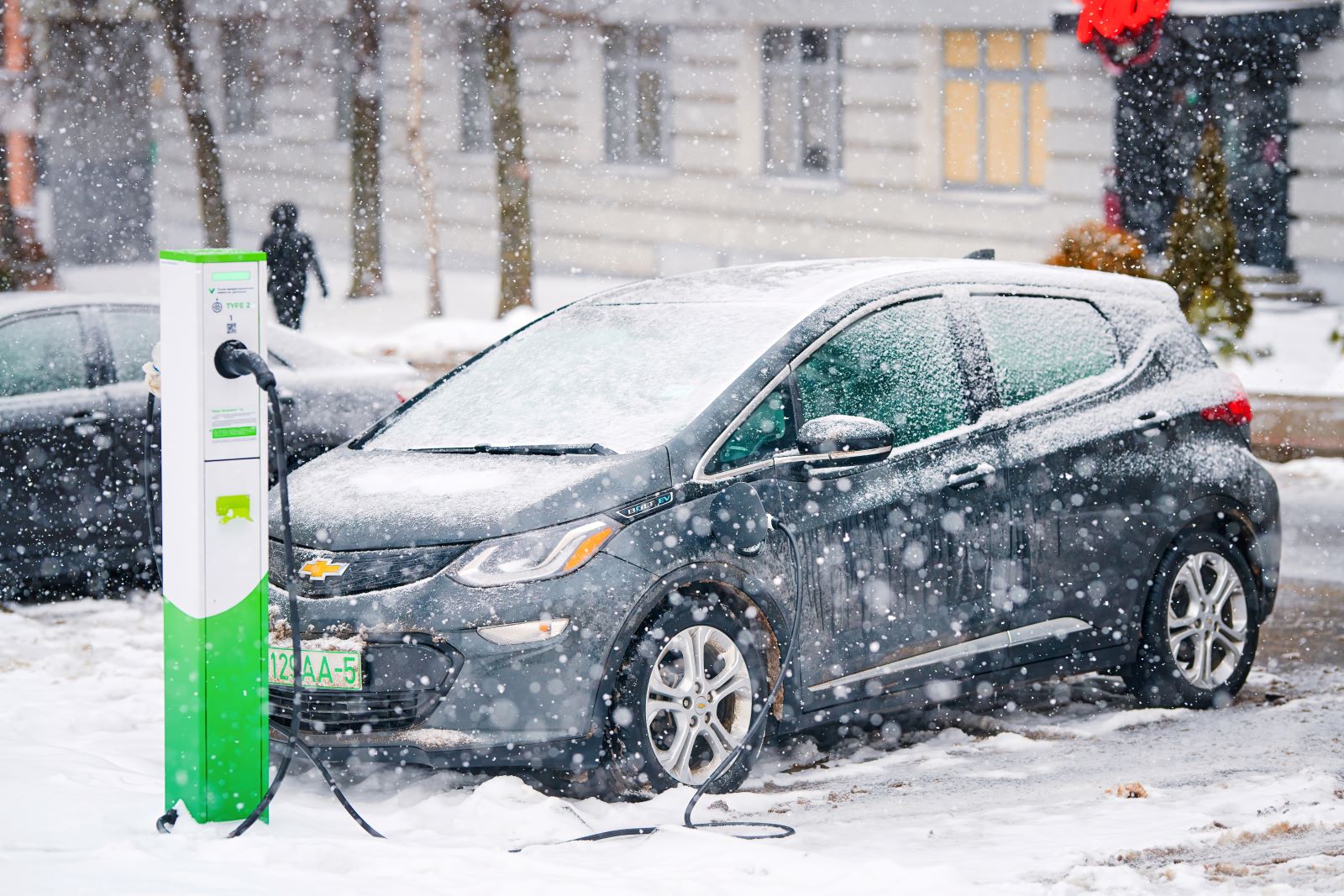

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Tricky_Shark
EV batteries take longer to charge in cold weather. According to a study from the Idaho National Laboratory, charging times in sub-freezing temperatures can take up to three times longer than in moderate conditions, frustrating drivers who rely on public charging stations during winter months.
20. Government Incentives Phasing Out

Image Credit: Shutterstock / chayanuphol
Federal tax credits and state incentives have helped reduce the cost of EV ownership, but many of these incentives are being phased out as the market matures. Tesla and General Motors, for instance, no longer qualify for the federal EV tax credit due to reaching sales caps, which means buyers will bear the full cost moving forward.
Is the Dream Worth the Price?

Image Credit: Shutterstock / Owlie Productions
The promise of electric vehicles is enticing, with lower emissions, less maintenance, and the allure of cutting-edge technology. However, the debate over their reliability continues as new challenges emerge.
Police Magnet: 7 Cars That Guarantee You’ll Get Pulled Over
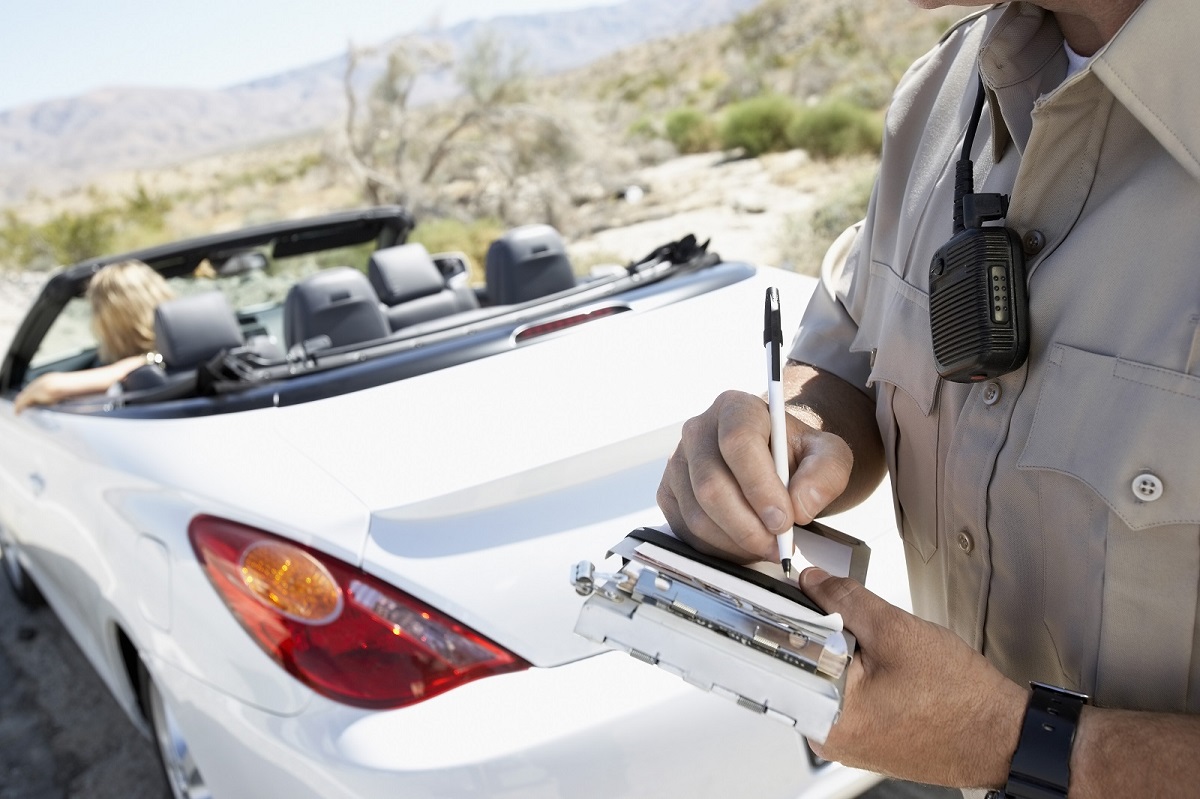

Image Credit: Shutterstock / sirtravelalot
Driving certain cars can make you more noticeable to law enforcement, even if you’re abiding by all the rules. Are you driving one of these “police magnets”? Here are seven cars that seem to attract more police attention than others. Police Magnet: 7 Cars That Guarantee You’ll Get Pulled Over
The Classic Cars That Were Total Clunkers

Image Credit: Pexels / Pixabay
Nostalgia has a funny way of making the past seem better than it was, especially when it comes to cars. But here’s the hard truth: some of those “classic” cars your dad raves about were real clunkers. Here’s a closer look at why some of those so-called “classics” weren’t all they were cracked up to be. The Classic Cars That Were Total Clunkers
The Worst U.S. Cars Ever Made: A Retro List

Image Credit: Pexels / Be The Observer
The U.S. auto industry has produced some incredible vehicles, but not every model was a hit. Here’s a look back at 16 of the worst cars ever made in the U.S., each infamous for its own unique flaws. The Worst U.S. Cars Ever Made: A Retro List
Featured Image Credit: Shutterstock / Owlie Productions.
The content of this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute or replace professional advice.
The images used are for illustrative purposes only and may not represent the actual people or places mentioned in the article.
For transparency, this content was partly developed with AI assistance and carefully curated by an experienced editor to be informative and ensure accuracy.



